肝母细胞瘤是一种罕见的恶性肝癌,发生于婴儿和儿童,由类似胎儿肝细胞,成熟肝细胞或胆管细胞的组织组成。 它们通常伴有腹部肿块。 这种疾病最常见于孩子出生后的前三年。[1] 甲胎蛋白(AFP)水平通常升高,但当AFP在诊断时未升高时,预后很差。[2]
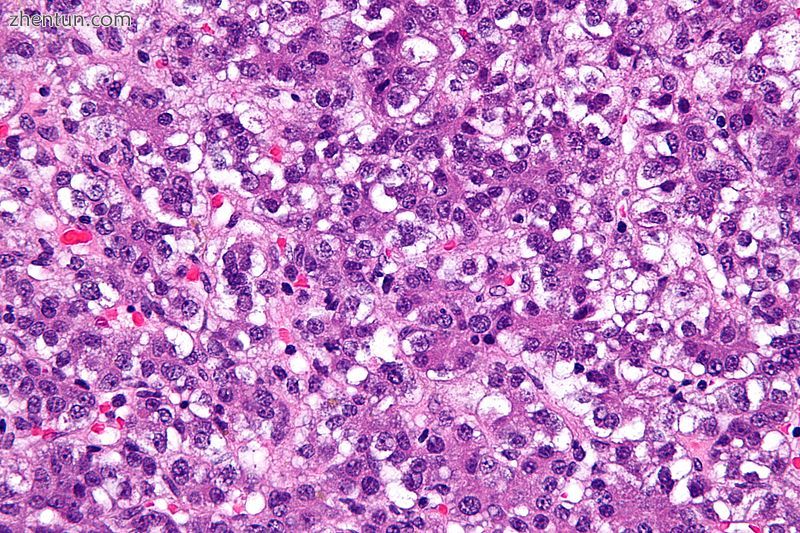
肝母细胞瘤的显微照片。 H&E染色。
目录
1 症状
2 病理生理学
3 诊断
4 治疗
5 参考
症状
患者在诊断时通常无症状[3]。 结果,疾病通常在诊断时发展。
病理生理学
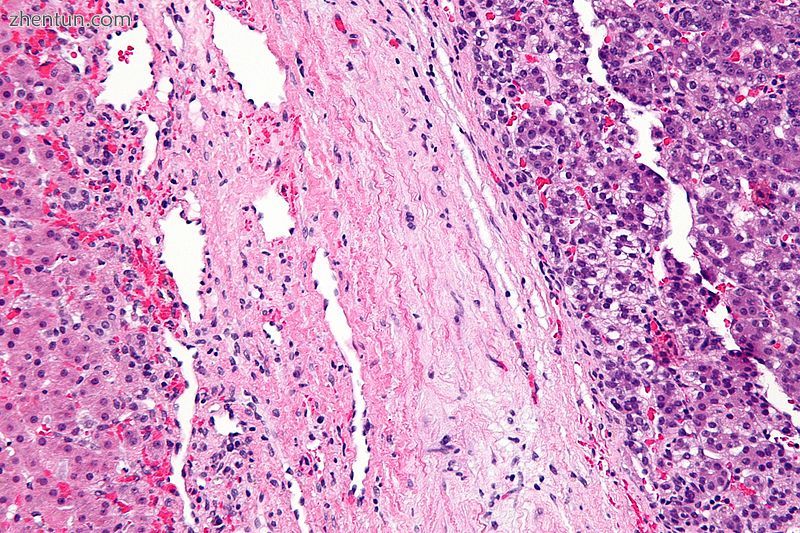
显微照片显示肝母细胞瘤(图像右侧)和正常肝脏(图像左侧)。 H&E染色。
肝母细胞瘤起源于未成熟的肝脏前体细胞,通常是单焦的,比左叶更频繁地影响肝右叶,并且可以转移。它们分为两种类型:“上皮型”和“混合上皮/间充质型”。
家族性腺瘤性息肉病(FAP),早发性结肠息肉和腺癌综合征患者,经常发生肝母细胞瘤[4] [5]。此外,β-catenin突变已被证实在散发性肝母细胞瘤中很常见,多达67%的患者发生[6] [7]。
最近,Wnt信号通路的其他成分也在肝母细胞瘤的原因中证明了该途径的组成性激活中的可能作用[7] [8],越来越多的证据表明肝母细胞瘤来源于多能干细胞[9]。
肝母细胞瘤发病率增加的综合征包括Beckwith Wiedmann综合征,18三体,21三体,Acardia综合征,Li-Fraumeni综合征,Goldenhar综合征,von Gierke病和家族性腺瘤性息肉病。 [10]
诊断
最常见的肝母细胞瘤检测方法是检查甲胎蛋白水平的血液检测。甲胎蛋白(AFP)用作生物标志物,以帮助确定儿童肝癌的存在。出生时,婴儿的AFP水平相对较高,到生命的第二年就会降到正常的成人水平。据报道,儿童AFP的正常水平低于50毫微克/毫升(ng / ml)和10 ng / ml的成人。 AFP水平大于500(ng / ml)是肝母细胞瘤的重要指标。 AFP也被用作治疗成功的指标。如果治疗成功消除癌症,预计AFP水平将恢复正常。[11]
治疗
手术切除肿瘤,肿瘤切除前的辅助化疗和肝移植已被用于治疗这些癌症。[12] [13] 原发性肝移植提供高,长期,无病生存率在80%的范围内,在完全肿瘤切除和辅助化疗的情况下,存活率接近100%。[14] [15] 转移的存在是预后不良的最强预测因子。[16]
参考:
http://hepatoblastoma.mditv.com/generalinfo[full citation needed]
De Ioris M, Brugieres L, Zimmermann A, Keeling J, Brock P, Maibach R, Pritchard J, Shafford L, Zsiros J, Czaudzerna P, Perilongo G (2007). "Hepatoblastoma with a low serum alpha-fetoprotein level at diagnosis: The SIOPEL group experience". Eur J Cancer. 44 (4): 545–50. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.11.022. PMID 18166449.
Willert, Jennifer. "Pediatric Hepatoblastoma Clinical Presentation: History, Physical, Causes". emedicine.medscape.com.
Hirschman BA, Pollock BH, Tomlinson GE (August 2005). "The spectrum of APC mutations in children with hepatoblastoma from familial adenomatous polyposis kindreds". J. Pediatr. 147 (2): 263–6. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.04.019. PMID 16126064.
Sanders RP, Furman WL (November 2006). "Familial adenomatous polyposis in two brothers with hepatoblastoma: implications for diagnosis and screening". Pediatr Blood Cancer. 47 (6): 851–4. doi:10.1002/pbc.20556. PMID 16106429.
Anna CH, Sills RC, Foley JF, Stockton PS, Ton TV, Devereux TR (June 2000). "Beta-catenin mutations and protein accumulation in all hepatoblastomas examined from B6C3F1 mice treated with anthraquinone or oxazepam". Cancer Res. 60 (11): 2864–8. PMID 10850429.
Tan, Xinping; Apte, Udayan; Micsenyi, Amanda; Kotsagrelos, Emorphia; Luo, Jian-Hua; Ranganathan, Sarangarajan; Monga, Dulabh K.; Bell, Aaron; Michalopoulos, George K.; Monga, Satdarshan P.S. (2005). "Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: A Novel Target of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Liver". Gastroenterology. 129 (1): 285–302. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.04.013. PMC 1821080. PMID 16012954.
Koch A, Waha A, Hartmann W, et al. (June 2005). "Elevated expression of Wnt antagonists is a common event in hepatoblastomas". Clin. Cancer Res. 11 (12): 4295–304. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1162. PMID 15958610.
Ruck P, Xiao JC (November 2002). "Stem-like cells in hepatoblastoma". Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 39 (5): 504–7. doi:10.1002/mpo.10175. PMID 12228907.
Zimmerman A, Saxena R. Hepatoblastoma. In: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System, 4th, Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND (Eds), IARC, Lyon 2010. p.229.
Sarto, I.; Klausberger, T.; Ehya, N.; Mayer, B.; Fuchs, K.; Sieghart, W. (2002). "A novel site on gamma 3 subunits important for assembly of GABA(A) receptors". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (34): 30656–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203597200. PMID 12065588.
Ang JP, Heath JA, Donath S, Khurana S, Auldist A (February 2007). "Treatment outcomes for hepatoblastoma: an institution's experience over two decades". Pediatr. Surg. Int. 23 (2): 103–9. doi:10.1007/s00383-006-1834-1. PMID 17119981.
Otte JB, Pritchard J, Aronson DC, et al. (January 2004). "Liver transplantation for hepatoblastoma: results from the International Society of Pediatric Oncology (SIOP) study SIOPEL-1 and review of the world experience". Pediatr Blood Cancer. 42 (1): 74–83. doi:10.1002/pbc.10376. PMID 14752798.
Pediatric Hepatoblastoma at eMedicine
Otte JB, de Ville de Goyet J, Reding R (October 2005). "Liver transplantation for hepatoblastoma: indications and contraindications in the modern era". Pediatr Transplant. 9 (5): 557–65. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3046.2005.00354.x. PMID 16176410.
Czauderna P, Mackinlay G, Perilongo G, et al. (June 2002). "Hepatocellular carcinoma in children: results of the first prospective study of the International Society of Pediatric Oncology group". J. Clin. Oncol. 20 (12): 2798–804. doi:10.1200/JCO.2002.06.102. PMID 12065556. |